SSH outbound connections – what are they trying?
Still fascinated by the outbound connection attempts from my Cowrie honeypot, I’ve been looking into what the intruders are trying to obtain with the outbound connections. As previously mentioned, there are bots actively attempting outbound connections towards a lot of remote services. Most are simply TCP socket connection attempts, but now and again the connection attempts hold payload data. Payload for encrypted services (SMTPS, HTTPS etc) is already encrypted. That leaves the plaintext services, mostly SMTP and HTTP.
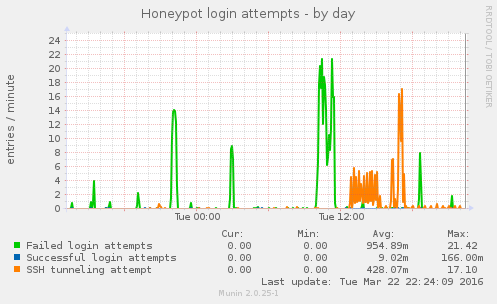
The following Munin graph shows today’s activity. At their busiest, the Russian bots performed outbound connection attempts at a rate of 17 attempts per minute (one per 3-4 seconds).
There are a few attempts to connect to mail servers. The following EHLO greetings, i.e. how the intruders try to introduce the honeypot when connecting, are among the ones observed:
EHLO essex1.com
EHLO garagedoorrepairelpaso-tx.com
EHLO tx.rr.com
EHLO xtreme-xposure.co.za
The remaining attempts described here are HTTP requests. The requests are for the web root (GET /) unless otherwise noted. All requests have more headers than what’s shown here, I’ve pruned the less interesting ones for readability.
The bots attempt several requests towards “check my IP” sites, perhaps to check connectivity and/or to detect the outside IP in a NATed environment:
Host: www.check2ip.com
Host: www.ip-score.com
Host: checkip.dyndns.com
GET /ip.php?i=193.169.52.210:14032 HTTP/1.1 Host: vlg97.ru Accept-Language: ru-RU,ru
GET /showmyip.php HTTP/1.1 Host: vipvpn.com
Then there are some attempts to reach URL shorteners. Ignoring the fact that these headers are crafted, the Google referers are obviously fake since a Google HTTPS search will not pass the referer to an HTTP site.
GET /make_url.php HTTP/1.1 Host: shorturl.com Referer: https://bitly.com/shorten
Host: is.gd Referer: https://bitly.com/shorten/
Host: is.gd Referer: http://bit.do/
Host: arurl.co Referer: https://www.google.com/search?q=http://arurl.co/
Host: scurteaza.link Referer: https://www.google.com/search?q=http://scurteaza.link/
POST /mod_perl/url-shortener.pl HTTP/1.1 X-Requested-With: XMLHttpRequest Host: bit.do Referer: http://bit.do/ Cookie: permasession=145xxxx290|pscxxxxzxq
They’re also trying to connect to Craigslist. These attempts have started to appear the last few days. Note: Parts of the URLs are obfuscated.
GET /reply/eau/m4w/548xxxx413 HTTP/1.1 Referer: http://eauclaire.en.craigslist.org/m4w/548xxxx413.html Host: eauclaire.en.craigslist.org X-Requested-With: XMLHttpRequest
GET /reply/evv/m4w/550xxxx297 HTTP/1.1 Host: evansville.en.craigslist.org Referer: http://evansville.en.craigslist.org/m4w/550xxxx297.html
GET /reply/hez/m4w/546xxxx191 HTTP/1.1 Host: batonrouge.craigslist.org User-Agent: Mozilla/5.0 (Nintendo WiiU) AppleWebKit/534.52 (KHTML, like Gecko) NX/2.1.0.10.9 NintendoBrowser/1.5.0.8047.EU Referer: http://batonrouge.craigslist.org/m4w/546xxxx191.html X-Requested-With: XMLHttpRequest
The function of the below connection attempts are still unexplored:
POST /GetSignedKey_new1.php HTTP/1.0 Connection: keep-alive Host: instabot.ru User-Agent: Instagram 5.0.0 Windows Phone (8.10.14147.180; 480x320; NOKIA; tAbd_apiM; uk_UA)
POST / HTTP/1.1 User-Agent: Mozilla/4.0 (compatible; MSIE 6.0; Windows NT 5.1; SV1) Host: work.a-poster.info data=cfaxxxxaebacbdaf
POST / HTTP/1.1 Host: work.a-poster.info data=cfbxxxxdeadecaa
Some statistics describing the honeypot activity the last few weeks, only counting the intruders that are also attempting outbound connections:
| Attempts | Originating IP |
|---|---|
| 13353 | 193.169.52.221 |
| 9816 | 193.169.52.214 |
| 6344 | 193.169.52.213 |
| 4246 | 193.169.52.220 |
| 620 | 193.169.52.211 |
| 435 | 193.169.52.212 |
| 105 | 193.169.52.210 |
| 17 | 193.201.225.84 |
| 6 | 193.201.227.200 |
| 5 | 193.201.227.52 |
| 2 | 193.201.227.8 |
| 2 | 193.201.227.70 |
| 1 | 193.201.227.18 |
| 1 | 125.212.232.210 |